Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible.

Java is a general-purpose, class-based, object-oriented programming language designed for having lesser implementation dependencies. It is a computing platform for application development. Java is fast, secure, and reliable, therefore. It is widely used for developing Java applications in laptops, data centers, game consoles, scientific supercomputers, cell phones, etc.
What is Java Platform?
Java Platform is a collection of programs that help programmers to develop and run Java programming applications efficiently. It includes an execution engine, a compiler, and a set of libraries in it. It is a set of computer software and specifications. James Gosling developed the Java platform at Sun Microsystems, and the Oracle Corporation later acquired it.
What is Java used for?
Here are some important Java applications:
It is used for developing Android Apps
Helps you to create Enterprise Software
Wide range of Mobile java Applications
Scientific Computing Applications
Use for Big Data Analytics
Java Programming of Hardware devices
Used for Server-Side Technologies like Apache, JBoss, GlassFish, etc.
History of Java Programming Language
Here are important landmarks from the history of the Java language:
The Java language was initially called OAK. Originally, it was developed for handling portable devices and set-top boxes. Oak was a massive failure. In 1995, Sun changed the name to "Java" and modified the language to take advantage of the burgeoning www (World Wide Web) development business. Later, in 2009, Oracle Corporation acquired Sun Microsystems and took ownership of three key Sun software assets: Java, MySQL, and Solaris. Java Versions Here are a brief history of all the Java versions with its release date.
Java Versions Release Date
JDK Alpha and Beta 1995
JDK 1.0 23rd Jan 1996
JDK 1.1 19th Feb 1997
J2SE 1.2 8th Dec 1998
J2SE 1.3 8th May 2000
J2SE 1.4 6th Feb 2002
J2SE 5.0 30th Sep 2004
Java SE 6 11th Dec 2006
Java SE 7 28th July 2011
Java SE 8 18th Mar 2014
Java SE 9 21st Sep 2017
Java SE 10 20th Mar 2018
JAVA SE 11 25th Sep 2018
JAVA SE 12 19th Mar 2019
JAVA SE 13 17th Sep 2019
JAVA SE 14 17th Mar 2020
JAVA SE 15 15th Sep 2020 (latest Java Version)
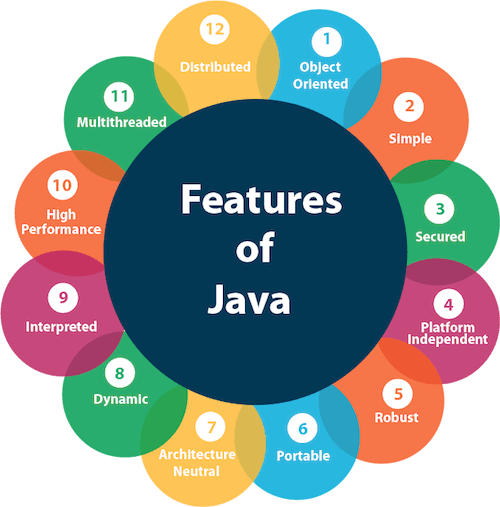
Java Features
Here are some important Java features:
It is one of the easy-to-use programming languages to learn. Write code once and run it on almost any computing platform. Java is platform-independent. Some programs developed in one machine can be executed in another machine. It is designed for building object-oriented applications. It is a multithreaded language with automatic memory management. It is created for the distributed environment of the Internet. Facilitates distributed computing as its network-centric. Components Of Java Programming Language A Java Programmer writes a program in a human-readable language called Source Code. Therefore, the CPU or Chips never understand the source code written in any programming language.
These computers or chips understand only one thing, which is called machine language or code. These machine codes run at the CPU level. Therefore, it would be different machine codes for other models of CPU.
However, you need to worry about the machine code, as programming is all about the source code. The machine understands this source code and translates them into machine understandable code, which is an executable code.

All these functionalities happen inside the following 3 Java platform components:
Java Development kit (JDK)
JDK is a software development environment used for making applets and Java applications. The full form of JDK is Java Development Kit. Java developers can use it on Windows, macOS, Solaris, and Linux. JDK helps them to code and run Java programs. It is possible to install more than one JDK version on the same computer.
Why use JDK?
Here are the main reasons for using JDK:
JDK contains tools required to write Java programs and JRE to execute them. It includes a compiler, Java application launcher, Appletviewer, etc. Compiler converts code written in Java into byte code. Java application launcher opens a JRE, loads the necessary class, and executes its main method. Java Virtual Machine (JVM): Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is an engine that provides a runtime environment to drive the Java Code or applications. It converts Java bytecode into machine language. JVM is a part of the Java Run Environment (JRE). In other programming languages, the compiler produces machine code for a particular system. However, the Java compiler produces code for a Virtual Machine known as Java Virtual Machine.
Why JVM? Here are the important reasons of using JVM:
JVM provides a platform-independent way of executing Java source code. It has numerous libraries, tools, and frameworks. Once you run a Java program, you can run on any platform and save lots of time. JVM comes with JIT (Just-in-Time) compiler that converts Java source code into low-level machine language. Hence, it runs faster than a regular application. Java Runtime Environment (JRE) JRE is a piece of software that is designed to run other software. It contains the class libraries, loader class, and JVM. In simple terms, if you want to run a Java program, you need JRE. If you are not a programmer, you don't need to install JDK, but just JRE to run Java programs.
Why use JRE?
Here are the main reasons of using JRE:
JRE contains class libraries, JVM, and other supporting files. It does not include any tool for Java development like a debugger, compiler, etc. It uses important package classes like math, swing, util, lang, awt, and runtime libraries. If you have to run Java applets, then JRE must be installed in your system. Different Types of Java Platforms There are four different types of Java programing language platforms:
Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE): Java SE's API offers the Java programming language's core functionality. It defines all the basis of type and object to high-level classes. It is used for networking, security, database access, graphical user interface (GUI) development, and XML parsing.
Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE): The Java EE platform offers an API and runtime environment for developing and running highly scalable, large-scale, multi-tiered, reliable, and secure network applications.
Java Programming Language Platform, Micro Edition (Java ME): The Java ME platform offers an API and a small-footprint virtual machine running Java programming language applications on small devices, like mobile phones.
Java FX: JavaFX is a platform for developing rich internet applications using a lightweight user-interface API. It user hardware-accelerated graphics and media engines that help Java take advantage of higher-performance clients and a modern look-and-feel and high-level APIs for connecting to networked data sources.
Java "Hello, World!" Program
// Your First Program
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}
Output
Hello, World!
Best Course to get started with Java